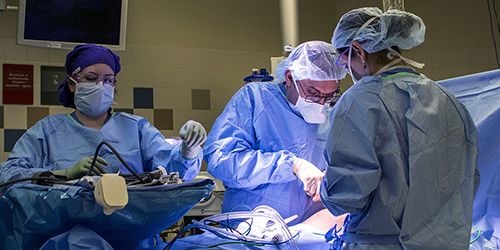
If you live with liver cancer treatment in Farmington the disease could already have spread to other areas of your body, such as the lungs and bones. To prevent this from happening, chemoembolization targets liver cancer — more specifically, cancer that originated in the liver or spread there from other areas in the body. This targeted therapy can help doctors slow down the progression of liver cancer while providing you with more time to live comfortably and enjoy life. Here’s what you need to know about chemoembolization, one of the newest treatments for liver cancer.
The Future of CE Procedures
Currently, chemotherapy is injected into a vein to get to cancer cells throughout your body. Chemotherapy often kills healthy cells in addition to cancerous ones, which may leave you with side effects like hair loss and fatigue. Chemoembolization targets liver cancer — more specifically, cancer that originated in the liver or spread there from other areas in Farmington
What is Chemotherapy Embolization (CE)?
liver cancer treatment Farmington (CE) is a treatment that uses a catheter to inject chemotherapy drugs into liver tumors in order to kill them. Targeted to treat liver cancer – especially metastatic liver cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma, CE delivers high doses of chemotherapy drugs specifically to these areas.
CE and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is a kind of liver cancer that originates in liver cells. It’s sometimes called liver cancer. HCC is treated differently than cancers originating in other organs. Other types of liver cancer are often treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy, but treatment may be different if you have HCC. Chemotherapy is also sometimes used for HCC, but it depends on where your cancer started. CE Versus Radioembolization (RE) One of the chemoembolization’s primary uses is to destroy cancerous tumors in other parts of a person’s body, particularly if those tumors have spread to or grown within a person’s liver. But these treatments can vary depending on where they are being administered. Here are some key differences between using chemoembolization to treat liver cancer and using radioembolization instead. CE Results
The success of chemoembolization is measured by its ability to reduce cancer cells. It’s common for patients to experience improvement in their symptoms and tests at first, but recurrence isn’t uncommon either. This therapy is generally not recommended as primary treatment because of those risks, but it may be used on top of surgery or other treatments. The size and number of tumors in your liver will affect what treatment options are available to you. Does Medicare Cover CE Procedures?
Medicare covers several chemoembolization procedures, but only when they are performed in addition to other treatments. Chemoembolization may also be covered by private insurance plans. Hospital Stay After a CE Procedure Once chemoembolization is complete, a patient may need to stay in a hospital for a day or two. The patient may also need to take anti-clotting medications and undergo tests to make sure their liver has not been harmed. If it has, they will likely need further treatments. The Future of CE Procedures
Currently, chemotherapy is injected into a vein to get to cancer cells throughout your body. Chemotherapy often kills healthy cells in addition to cancerous ones, which may leave you with side effects like hair loss and fatigue. Chemoembolization targets liver cancer — more specifically, cancer that originated in the liver or spread there from other areas in Farmington.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is a kind of liver cancer that originates in liver cells. It’s sometimes called liver cancer. HCC is treated differently than cancers originating in other organs. Other types of liver cancer are often treated with surgery and/or radiation therapy, but treatment may be different if you have HCC. Chemotherapy is also sometimes used for HCC, but it depends on where your cancer started. CE Versus Radioembolization (RE) One of the chemoembolization’s primary uses is to destroy cancerous tumors in other parts of a person’s body, particularly if those tumors have spread to or grown within a person’s liver. But these treatments can vary depending on where they are being administered. Here are some key differences between using chemoembolization to treat liver cancer and using radioembolization instead. CE Results
The success of chemoembolization is measured by its ability to reduce cancer cells. It’s common for patients to experience improvement in their symptoms and tests at first, but recurrence isn’t uncommon either. This therapy is generally not recommended as primary treatment because of those risks, but it may be used on top of surgery or other treatments. The size and number of tumors in your liver will affect what treatment options are available to you. Does Medicare Cover CE Procedures?
Medicare covers several chemoembolization procedures, but only when they are performed in addition to other treatments. Chemoembolization may also be covered by private insurance plans. Hospital Stay After a CE Procedure Once chemoembolization is complete, a patient may need to stay in a hospital for a day or two. The patient may also need to take anti-clotting medications and undergo tests to make sure their liver has not been harmed. If it has, they will likely need further treatments. The Future of CE Procedures
Currently, chemotherapy is injected into a vein to get to cancer cells throughout your body. Chemotherapy often kills healthy cells in addition to cancerous ones, which may leave you with side effects like hair loss and fatigue. Chemoembolization targets liver cancer — more specifically, cancer that originated in the liver or spread there from other areas in Farmington.