The Portrayal of the Vault
A focal various leveled data set utilized in Windows 98, Windows CE, Windows NT, and Windows 2000 is used to store data that is important to design the framework for at least one client, application, and equipment gadget.
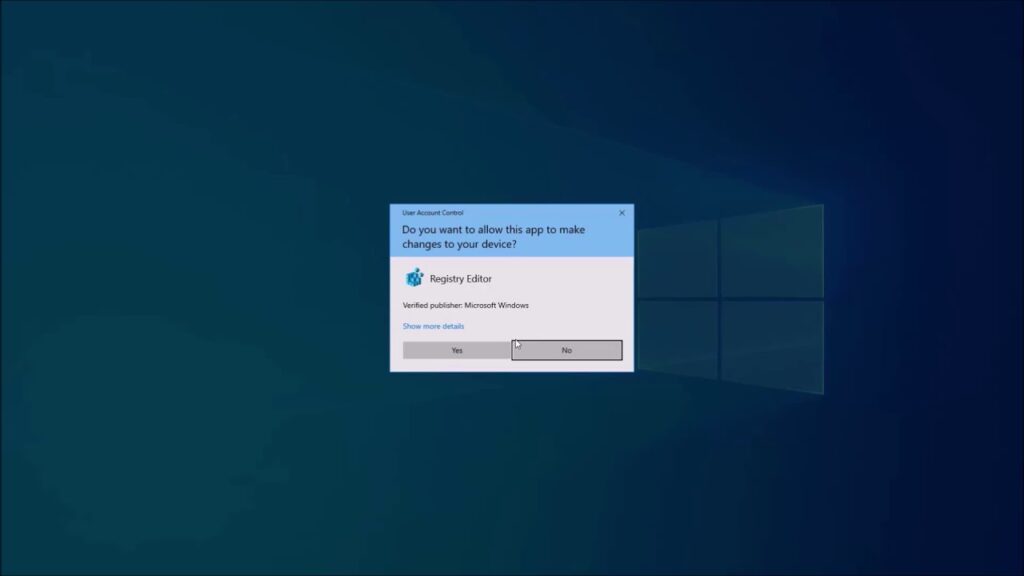
The Registry contains data that Windows constantly references during activity, for example, profiles for every client, the applications introduced on the PC, and the kinds of reports that each can make Use the Windows Registry Editor, property sheet settings for envelopes, and application symbols, and what equipment exists on the framework, and the ports that are being utilized. If you want to use the window registry editor then do this.
The Registry replaces the majority of the text-based .ini records that are utilized in Windows 3. x and MS-DOS setup documents, like the Autoexec.bat and Config. sys. Albeit the Registry is normal to a few Windows working frameworks, there are a few distinctions among them. A library hive is a gathering of keys, subkeys, and values in the vault that has a bunch of supporting documents that contain reinforcements of its information. The supporting records for all hives with the exception of HKEY_CURRENT_USER are in the %SystemRoot%\System32\Config organizer on Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, and Windows Vista. The supporting records for HKEY_CURRENT_USER are in the %SystemRoot%\Profiles\Username envelope. The record name augmentations of the documents in these envelopes show the kind of information that they contain. Likewise, the absence of an expansion may at times show the kind of information that they contain.
Back up the vault
Before you alter the vault, send out the keys in the library that you intend to alter, or back up the entire vault. In the event that an issue happens, you can follow the means in the Restore the vault segment to reestablish the library to its past state. To back up the entire vault, go through the Backup utility to back to the framework state. The framework state incorporates the vault, the COM+ Class Registration Database, Use the Windows Registry Editor, and your boot records. For more data about how to go through the Backup utility to back the framework state, see the accompanying articles:
Back up and Reestablish your PC
The most effective method to utilize the reinforcement component to back up and reestablish information in Windows Server 2003
To change vault information, a program should utilize the library works that are characterized in Registry Functions.
Executives can alter the vault by utilizing Registry Editor (Regedit.exe or Regedt32.exe), Group Policy, System Policy, Registry (.reg) records, or by running contents, for example, VisualBasic script documents.
Utilize the Windows UI
We suggest that you utilize the Windows UI to change your framework settings rather than physically altering the vault. Be that as it may, altering the library may in some cases be the best strategy to determine an item issue. Assuming the issue is recorded in the Microsoft Knowledge Base, an article with bit-by-bit directions to alter the vault for that issue will be accessible. We suggest that you adhere to those guidelines precisely.
Use Registry Editor
Difficult issues could happen on the off chance that you alter the vault mistakenly by utilizing Registry Editor or by utilizing another strategy. These issues could expect that you reinstall the working framework. Microsoft can’t ensure that these issues can tackled. Change the vault despite the obvious danger.
You can utilize Registry Editor to do the accompanying activities:
- Find a subtree, key, subkey, or esteem
- Add a subkey or a worth
- Change a worth
- Erase a subkey or a worth
- Rename a subkey or a worth
The routing area of Registry Editor shows organizers. Every organizer addresses a predefined key on the neighborhood PC. At the point when you access the library of a far-off PC, just two predefined keys show up: HKEY_USERS and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.
Use Group Policy
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) has managerial apparatuses that you can use to oversee networks, PCs, administrations, and other framework parts. The Group Policy MMC snap-in allows managers to characterize strategy settings that applied to PCs or clients. You can carry out Group Policy on nearby PCs by utilizing the neighborhood Group Policy MMC snap-in, Gpedit.MSC. You can execute Group Policy in Active Directory by utilizing the Active Directory Users and Computers MMC snap-in. Use the Windows Registry Editor For more data about how to utilize Group Policy, see the Help subjects in the fitting Group Policy MMC snap-in.
Utilize a Registration Entries
Make a Registration Entries (.reg) record that contains the library changes, and afterward run the .reg document on the PC where you need to roll out the improvements. You can run the .reg document physically or by utilizing a logon script. For more data.
Use Windows Management Instrumentation
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is a part of the Microsoft Windows working framework and is the Microsoft execution of Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM). WBEM is an industry drive to foster a standard innovation for getting to the executive’s data in an undertaking climate. You can utilize WMI to computerize regulatory errands (like altering the vault) in a venture climate.