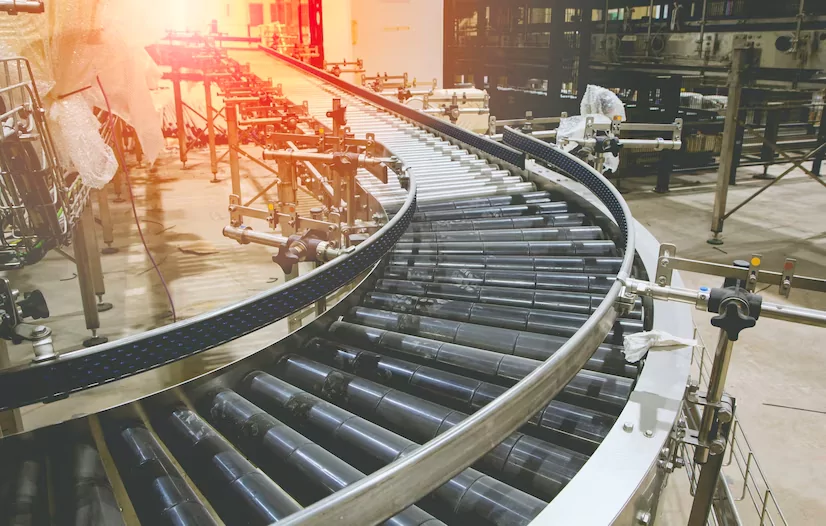
Steel manufacturing is a complex and high-temperature process that demands precision and efficiency. In this intricate dance of molten metal and intense heat, various components play crucial roles, and among them, heat-resistant belts stand out as unsung heroes.
These belts, often overlooked but indispensable, play a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless operation of steel manufacturing processes.
This article delves into the significance of heat-resistant belts in the steel industry, exploring their functions, types, and the impact they have on the overall efficiency and safety of steel production.
Basics of Steel Manufacturing
Before delving into the specifics of heat-resistant belts, it’s essential to understand the basics of steel manufacturing. The process involves the extraction of raw materials, such as iron ore and coal, which are then transformed through a series of intricate steps.
The primary stages include ironmaking, steelmaking, and finishing. In these processes, extreme temperatures are a norm, and managing them efficiently is vital for the production of high-quality steel.
Role of Heat-Resistant Belts
Heat-resistant belts play a crucial role in steel manufacturing by ensuring the safe and efficient transport of materials through high-temperature processes such as cooling, annealing, and forging.
These belts are designed to withstand extreme heat and provide reliable performance, contributing to the overall productivity and quality of the steel manufacturing process.
1. Conveying Raw Materials
One of the primary functions of heat-resistant belts in steel manufacturing is the transportation of raw materials.
From the extraction of iron ore to the delivery of coke and limestone to the blast furnace, these belts facilitate the movement of heavy and abrasive materials.
Heat-resistant belts ensure the smooth and continuous flow of raw materials, preventing disruptions in the early stages of steel production.
2. Handling Molten Metal
As the raw materials undergo transformation in the blast furnace, molten metal is produced. Heat-resistant belts are crucial in transporting this molten metal safely and efficiently.
The ability of these belts to withstand high temperatures is paramount during this phase, as any failure in the conveyor system could lead to significant safety hazards and production delays.
Advantages of Heat-Resistant Belts
Heat-resistant belts offer several advantages in steel manufacturing, including the ability to withstand high temperatures, reduce maintenance costs, increase productivity, and ensure the safe and efficient transportation of materials throughout the production process.
1. Extended Equipment Lifespan
The use of heat-resistant belts contributes to the extended lifespan of conveyor systems in steel manufacturing plants. These belts are specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions, minimizing wear and tear.
As a result, the need for frequent replacements is reduced, leading to cost savings and improved overall equipment reliability.
2. Enhanced Safety
Safety is paramount in the steel industry, where workers are exposed to challenging conditions. Heat-resistant belts, by virtue of their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, contribute to a safer working environment.
This is particularly critical when handling molten metal or operating in areas where heat-related accidents are a constant risk. The reliability of heat resistant conveyor belts ensures the smooth and secure movement of materials, minimizing the likelihood of accidents.
Industry professionals seeking firsthand insights into the robust safety measures and advanced technology in steel manufacturing can take a visit to this site.
3. Increased Operational Efficiency
The implementation of heat-resistant belts directly correlates with increased operational efficiency in steel manufacturing. By preventing unexpected breakdowns and reducing downtime, these belts contribute to a more streamlined production process.
The continuous and reliable movement of materials ensures that the various stages of steel manufacturing progress seamlessly, ultimately leading to higher production outputs and improved profitability.
Types of Heat-Resistant Belts
There are several types of heat-resistant belts used in steel manufacturing. These belts are essential for conveying hot materials and withstanding high temperatures in the steel manufacturing process.
1. Textile Reinforced Belts
Textile-reinforced heat-resistant belts are commonly used in steel manufacturing. These belts are made from various fibers, such as aramid and fiberglass, which provide strength and flexibility.
They are suitable for conveying lighter loads at moderate temperatures and are often used in the initial stages of the steelmaking process.
2. Steel Cord Reinforced Belts
In applications where higher tensile strength is required, steel cord reinforced heat-resistant belts come into play. These belts are equipped with steel cables embedded in the rubber matrix, providing superior strength and durability.
They are ideal for conveying heavy loads, especially in areas where high temperatures and abrasive materials are prevalent.
3. Specialty Coatings
Some heat-resistant belts come with specialty coatings to enhance their performance. These coatings may include materials like neoprene or silicone, which provide additional heat resistance and protection against wear and tear.
Specialty-coated belts are often used in critical areas of the steel manufacturing process where extreme conditions are prevalent.
Challenges in Steel Manufacturing
Steel manufacturing poses numerous challenges, with high temperatures, heavy loads, and abrasive materials being major concerns.
Heat-resistant belts play a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations by withstanding extreme heat and providing durability.
1. High Temperatures and Thermal Stress
One of the significant challenges in steel manufacturing is the extreme temperatures involved in various stages of the process. The equipment, including conveyor belts, is exposed to thermal stress, leading to wear and deterioration over time.
Heat-resistant belts play a crucial role in mitigating these challenges, ensuring the longevity of the conveyor system and preventing unexpected failures.
2. Abrasive Materials
The raw materials used in steel manufacturing, such as iron ore and coke, can be highly abrasive. Conventional belts may succumb to the abrasive nature of these materials, leading to frequent replacements and increased downtime.
Heat-resistant belts, designed to withstand abrasion, offer a solution to this challenge, reducing maintenance costs and improving efficiency.
Conclusion
The importance of heat-resistant belts in steel manufacturing cannot be overstated. These often-overlooked components play a crucial role in the transportation of raw materials, handling molten metal, and overcoming the challenges posed by extreme temperatures and abrasive materials.
The choice of the right type of heat-resistant belt is key to ensuring the longevity of conveyor systems, enhancing safety, and increasing operational efficiency in steel plants.