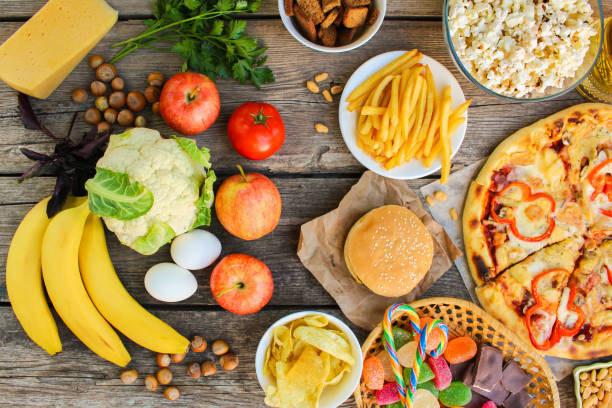
Nutrient rich foods play a positive role in promoting and sustaining a healthy lifestyle. These foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and other bioactive compounds crucial for the human body’s proper functioning.
Nutrient rich foods, on the other hand, give your body the building blocks it needs for good health and well-being, unlike empty-calorie foods like highly processed snacks and sugary drinks.
Consuming a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods ensures that the body receives a balanced supply of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals).
How to Add Nutrient Rich Foods to Your Healthy Eating Plan
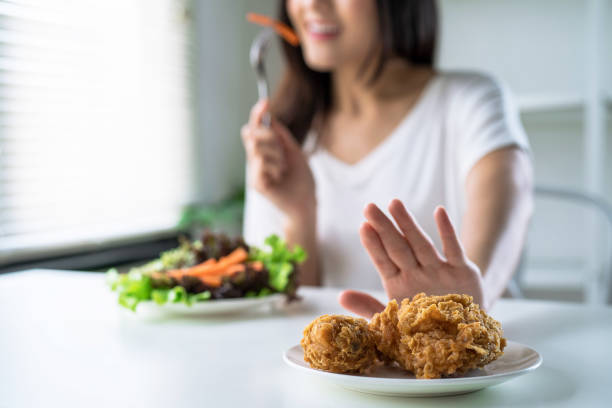

To make a healthy eating plan, you need to include foods that are high in nutrients and provide necessary vitamins, minerals, and other good compounds. Here are some useful tips to help you add more nutrient-dense foods to your diet:
1- Prioritize Whole Foods:
Emphasize whole, minimally processed foods in your diet. Choose whole grains, fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats over highly processed and refined options.
2- Choose Whole Grains:
Replace refined grains with whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat. Whole grains offer more fiber, vitamins, and minerals compared to their refined counterparts.
3- Prioritize Plant-Based Foods:
Increase the proportion of plant-based foods in your meals. Plant-based options like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes are rich in nutrients and associated with numerous health benefits.
4- Plan Balanced Meals:
Structure your meals to include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This balance helps regulate blood sugar levels and provides sustained energy throughout the day.
5- Add Healthy Fats:
Eat foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil that are high in healthy fats. These Nutrient rich foods and fats give you important fatty acids and help you feel full, which is good for your health in general.
keep yourself updated with this helpful SCP health portal
Different categories of essential nutrients
Essential nutrients are substances the body requires for normal physiological functioning but cannot produce in sufficient amounts. These nutrients must be obtained through the diet. Essential nutrients can be broadly categorised into six main groups:
Proteins:
Proteins are composed of amino acids essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting the immune system. Protein sources include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels various bodily functions. Carbohydrates can be simple (found in sugars) or complex (found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables). Whole, unprocessed carbohydrate sources are generally more nutrient-dense.
Fats:
Fats play a crucial role in energy storage, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). Healthy fat sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish, and plant-based oils. It’s essential to focus on unsaturated fats while limiting saturated and trans fats.
Vitamins:
Vitamins are organic compounds that regulate various physiological processes. They can be water-soluble (e.g., vitamin C, B-complex vitamins) or fat-soluble (e.g., vitamins A, D, E, K). Each vitamin has specific functions, and a diverse diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins ensures an adequate intake.
Minerals:
Minerals are inorganic elements necessary for various bodily functions, including bone health, nerve transmission, and fluid balance. Examples include calcium, potassium, sodium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and selenium. A balanced diet that includes a variety of foods is essential to meet mineral requirements.
Water:
While not a nutrient in the traditional sense, water is vital for life. It is involved in almost every bodily function, including digestion, nutrient transport, and temperature regulation. Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for overall health.
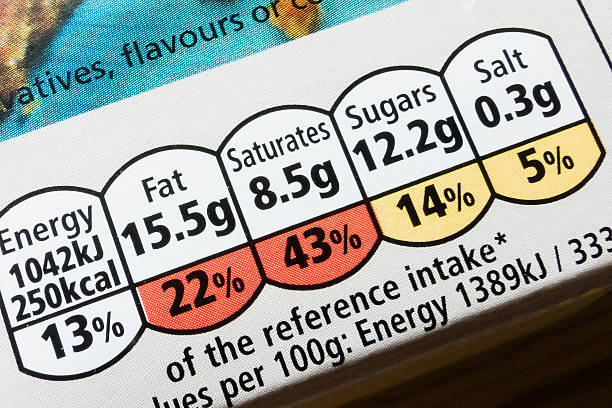
The USDA says that the following micronutrients may not be getting enough people in the United States.
- Calcium: Nonfat and low-fat dairy, dairy substitutes, broccoli, dark, leafy greens, and sardines
- Magnesium: Spinach, black beans, peas, and almonds
- Vitamin E: Whole-grain foods, nuts, seeds, avocados, spinach, and other dark leafy greens
- Vitamin C: Grapefruit, oranges, kiwis, cabbage, tomatoes, and red and green bell peppers
Importance of Incorporating Nutrient-Rich Foods
Benefits for Physical Health
1- Boosting Immune System:
Nutrient-rich foods are essential for supporting a robust immune system. Vitamins and minerals, such as vitamins C, D, zinc, and antioxidants, play crucial roles in immune function. Regularly consuming fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-dense foods helps the body defend against infections and illnesses.
2- Supporting Weight Management:
Nutrient-rich foods are often lower in calories and higher in fibre, promoting satiety and helping with weight management. These foods provide essential nutrients without the excess calories often found in processed and sugary options. A balanced diet of whole foods contributes to maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions.
3- Enhancing Energy Levels:
The body requires a consistent supply of nutrients to produce energy efficiently. Nutrient-rich foods, especially those rich in complex carbohydrates, proteins, and essential fats, provide sustained energy. Unlike sugary snacks that lead to energy spikes and crashes, nutrient-dense options support stable energy levels throughout the day.
Cognitive Benefits
1- Impact on Brain Function:
Nutrient-rich foods play a vital role in supporting optimal brain function. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, antioxidants in berries, and vitamins like B-complex vitamins contribute to cognitive health. These nutrients aid in memory, concentration, and overall brain performance, promoting mental clarity and sharpness.
2- Mood Regulation:
The connection between nutrition and mental health is significant. Nutrient-rich foods can influence neurotransmitter function and the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation. Eating lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins has been linked to a lower risk of depression and anxiety, which is good for your general mental health.
Key Takeaways
Incorporating nutrient rich foods into your diet is not just about meeting nutritional requirements; it is a holistic approach to promoting overall health. These foods help keep your immune system strong, help you control your weight, and give you more energy. Moreover, the impact on cognitive function, including improved brain function and mood regulation, highlights the profound connection between nutrition and mental well-being. Making informed food choices by prioritising nutrient-dense options can lead to a healthier and more vibrant life.