In today’s fast-paced digital world, businesses can no longer rely on guesswork when it comes to designing websites, applications, or digital products. Users expect seamless experiences that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive, efficient, and relevant to their needs. To meet these expectations, organizations must rely on UX research & analysis—the essential backbone of successful user experience design.
UX research and analysis are more than just design steps; they are strategic processes that uncover how users think, behave, and interact with digital products. This understanding allows designers, developers, and businesses to make informed decisions that lead to user-centered, data-driven, and impactful designs.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of UX research & analysis—exploring what it is, why it matters, the key methods used, and how it shapes modern digital innovation.
1. What is UX Research & Analysis?
UX research (User Experience research) is the systematic study of users and their interactions with products to understand their needs, motivations, pain points, and behavior patterns. It helps identify what users want, how they navigate, and where they face difficulties.
UX analysis, on the other hand, interprets the findings from research to extract actionable insights. It involves studying the collected data to determine what works well and what needs improvement in the product’s design, structure, or functionality.
Together, UX research & analysis create a foundation for informed design decisions. Instead of relying on assumptions or aesthetics alone, designers use real data to craft products that solve real problems effectively.
2. The Importance of UX Research & Analysis
Without proper research and analysis, even the most beautiful design can fail. A product that doesn’t resonate with users or meet their needs will quickly lose engagement, conversions, and loyalty. Let’s explore why UX research & analysis are vital:
a. Understanding User Needs
UX research allows businesses to empathize with their audience. By studying user behavior, preferences, and challenges, companies gain a deeper understanding of what their users truly need—not just what they say they want.
b. Reducing Design Risks
Guesswork often leads to costly redesigns or product failures. Research-based design minimizes risk by validating ideas before development, saving both time and money.
c. Enhancing Usability and Satisfaction
Through UX research & analysis, designers uncover usability issues that frustrate users. Fixing these issues leads to smoother interactions, increased satisfaction, and stronger user retention.
d. Boosting Conversions
When users find a product easy to use and aligned with their goals, conversion rates naturally rise. Every improvement—whether in navigation, layout, or messaging—can directly influence revenue.
e. Strengthening Brand Loyalty
Great user experiences create trust. A product that feels intuitive and reliable encourages repeat usage and positive word-of-mouth.
3. The Core Stages of UX Research & Analysis
To understand the process, it’s helpful to break it down into clear, structured stages:
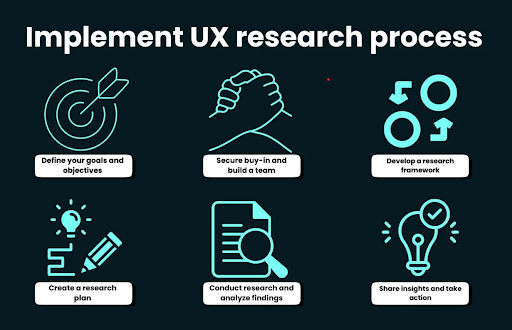
Stage 1: Define Goals and Hypotheses
Before any research begins, the team identifies clear objectives. What are you trying to learn? What assumptions do you want to validate or challenge? Defining research goals ensures efforts remain focused and measurable.
For example:
How do users navigate our checkout process?
Why are users abandoning our mobile app after the first session?
What features do users value most in a dashboard?
Stage 2: Choose Research Methods
The choice between qualitative and quantitative methods depends on the goals. Qualitative research explores “why” users behave a certain way, while quantitative data reveals “how much” or “how often.”
Stage 3: Collect Data
Once the plan is set, the research team gathers data through observations, interviews, surveys, and analytics tools.
Stage 4: Analyze and Interpret
After data collection, researchers look for trends, patterns, and correlations. This analysis phase turns raw information into insights that guide design decisions.
Stage 5: Apply Insights to Design
The final step is translating findings into actionable improvements. Whether redesigning a layout, adding new features, or refining content, UX analysis ensures every decision is backed by data.
4. Key UX Research Methods
To get accurate and valuable insights, UX researchers employ a mix of research methods. Each method provides a unique perspective on user behavior and experience.
1. User Interviews
One of the most powerful qualitative methods, interviews involve one-on-one conversations with real users. This approach uncovers motivations, challenges, and emotional responses that quantitative data can’t capture.
2. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys collect insights from a larger audience. They’re useful for validating patterns observed in smaller qualitative studies and gathering demographic or behavioral data.
3. Usability Testing
This method involves observing users as they complete tasks on a product. Researchers note where users struggle, hesitate, or make errors, helping designers identify usability problems that hinder performance.
4. Heuristic Evaluation
Experts evaluate the interface against recognized usability principles (heuristics). It’s a fast, cost-effective way to identify design flaws before testing with users.
5. A/B Testing
Two versions of a design are compared to see which performs better. A/B testing provides quantifiable data on which design choices drive higher engagement or conversions.
6. Analytics and Heatmaps
Tools like Google Analytics or Hotjar reveal how users interact with a website or app—showing click patterns, scroll depth, and drop-off points.
7. Card Sorting and Tree Testing
These methods help optimize information architecture by studying how users categorize and locate content.
8. Contextual Inquiry
Researchers observe users in their natural environment while using the product. This approach provides context that helps identify real-world obstacles.
5. Types of UX Research: Generative vs. Evaluative
UX research typically falls into two categories—generative and evaluative—each serving a distinct purpose.
Generative Research
This type of research helps identify new opportunities and user needs before a design is created. It answers questions like:
What problems are users facing?
What are their goals or frustrations?
Methods include interviews, field studies, and ethnographic research.
Evaluative Research
Evaluative research tests how well a design meets user needs. It’s conducted after prototypes or products are developed.
It answers questions like:
Can users easily complete tasks?
Is the interface intuitive?
Methods include usability testing, A/B testing, and analytics.
6. The Role of UX Analysis
While research focuses on gathering data, UX analysis focuses on making sense of that data. This involves synthesizing information, identifying insights, and recommending design improvements.
a. Data Synthesis
After research, raw data is categorized into themes, patterns, and user segments. Tools like affinity diagrams help visualize connections between insights.
b. Persona Creation
UX analysts often create user personas—fictional characters representing typical user types. Personas guide design decisions by keeping user needs front and center.
c. Journey Mapping
A user journey map visualizes how users interact with a product from start to finish, highlighting emotions, touchpoints, and pain areas.
d. Problem Identification
Through UX analysis, teams can pinpoint usability bottlenecks, confusing layouts, or missing functionalities.
e. Insight Translation
Finally, UX analysts turn insights into practical design recommendations that align with both user needs and business goals.
7. How UX Research & Analysis Improve Digital Products
The true value of UX research & analysis lies in its ability to transform insights into measurable improvements. Let’s explore how it impacts digital product performance.
a. Increases Engagement
By understanding what attracts and retains users, businesses can design engaging interfaces that keep audiences coming back.
b. Streamlines Navigation
Research uncovers how users move through your site or app, allowing designers to create intuitive navigation structures that minimize confusion.
c. Enhances Accessibility
Through user testing and analysis, teams identify barriers for users with disabilities and design solutions that make products more inclusive.
d. Improves Conversion Funnels
UX analysis highlights where users drop off in the sales or sign-up funnel, helping businesses make adjustments that increase conversion rates.
e. Strengthens Customer Trust
When users consistently experience ease, efficiency, and delight, they develop a sense of trust and loyalty toward your brand.
8. The Connection Between UX Research, Design, and Business Strategy
UX research doesn’t exist in isolation—it intersects with brand strategy, marketing, and technology. Companies that embrace UX research as part of their decision-making process often outperform competitors in customer satisfaction and ROI.
a. Informed Decision-Making
Research provides evidence-based insights that inform strategic decisions, from product features to marketing campaigns.
b. Reduced Development Costs
Fixing usability issues during the research phase is far cheaper than making changes after launch.
c. Data-Driven Innovation
UX research & analysis uncover unmet user needs, inspiring innovation and new product opportunities.
d. Alignment Across Teams
When everyone—from designers to developers to stakeholders—works from the same research insights, it ensures consistent, user-focused collaboration.
9. The Tools That Power UX Research & Analysis
Modern UX professionals rely on a variety of tools to conduct and analyze research efficiently:
User Testing, Maze, or Lookback: For remote usability testing.
Hotjar, Crazy Egg: For heatmaps and session recordings.
Figma, Miro, or FigJam: For creating user flows, journey maps, and affinity diagrams.
Google Analytics, Mixpanel: For quantitative analysis of user data.
Optimal Workshop: For information architecture testing (card sorting, tree testing).
These tools streamline data collection and visualization, enabling teams to focus on insights rather than logistics.
10. Common Mistakes to Avoid in UX Research & Analysis
Even skilled teams can make errors that compromise the quality of research. Here are a few pitfalls to avoid:
Skipping Research: Many businesses rush into design without understanding users first. This leads to poor usability and wasted resources.
Bias in Sampling: Interviewing only internal teams or limited user groups can distort findings.
Ignoring Quantitative Data: Relying solely on opinions without numerical validation can lead to misleading conclusions.
Poor Documentation: Without detailed documentation, valuable insights can be lost between research and development.
No Continuous Research: User needs evolve, so research should be ongoing—not a one-time task.
11. The Future of UX Research & Analysis
As technology and user behavior evolve, so too does the field of UX research. Future trends include:
AI-Driven Insights
Artificial intelligence can process vast datasets, uncovering hidden patterns and predicting user behavior more accurately than ever.
Emotion Analytics
Using facial recognition and sentiment analysis, researchers can measure users’ emotional responses during interactions.
Mixed Reality Testing
As AR and VR become mainstream, UX research will expand into virtual environments, testing spatial and sensory interactions.
Continuous Feedback Loops
Real-time analytics and user feedback systems will make UX research a dynamic, ongoing process integrated into every design phase.
12. Real-World Examples of UX Research in Action
Example 1: Netflix
Netflix heavily relies on UX research & analysis to refine its recommendation engine. By studying viewer habits, they tailor experiences for each user—resulting in increased watch time and customer satisfaction.
Example 2: Airbnb
Airbnb’s success is built on user research. By understanding traveler and host pain points, they designed intuitive booking flows and trust-building features like verified reviews.
Example 3: Google Maps
Through continuous usability testing and data analysis, Google Maps evolved to include predictive routing, local recommendations, and offline access—all inspired by real user feedback.
These examples demonstrate how data-driven UX practices can shape products that dominate their industries.
13. Building a Culture of UX Research & Analysis
For lasting success, UX research shouldn’t be treated as a one-time project. It must become part of an organization’s culture. Here’s how businesses can achieve that:
Educate Teams: Encourage non-design departments to understand the value of UX insights.
Integrate Research Early: Involve UX researchers from the ideation phase, not just after design begins.
Invest in Tools and Talent: Equip teams with proper tools and hire skilled UX researchers.
Foster Collaboration: Designers, developers, marketers, and analysts should work together based on shared research data.
Measure Impact: Regularly evaluate how UX improvements affect KPIs such as conversions, retention, and satisfaction.
14. Conclusion: UX Research & Analysis—The Key to User-Centric Success
In a digital era where user expectations are higher than ever, UX research & analysis have become indispensable tools for creating successful, human-centered products. They bridge the gap between what businesses want to offer and what users truly need.
By investing in solid research, analyzing data intelligently, and applying findings to design, companies can reduce risk, enhance satisfaction, and foster loyalty. It’s not just about making interfaces look better—it’s about ensuring every interaction feels natural, meaningful, and valuable.
Whether you’re launching a new product or improving an existing one, UX research and analysis provide the clarity, direction, and confidence you need to deliver exceptional digital experiences that stand the test of time.