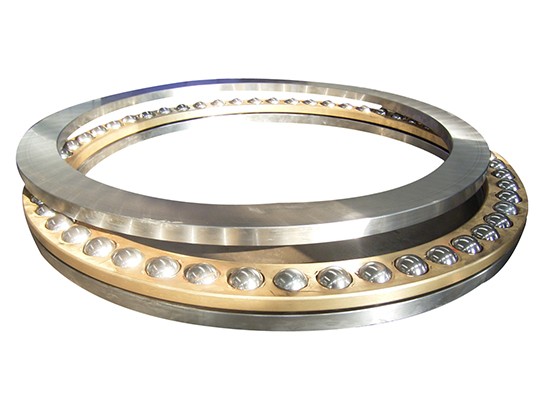
Thrust ball bearings are designed to withstand thrust loads during high-speed operation, and consist of a washer-like ferrule with a ball-rolling raceway groove. Since the ferrule is in the form of a seat cushion, the thrust ball bearing is divided into two types: flat seat cushion type and self-aligning spherical seat cushion type. In addition, this bearing can withstand axial loads, but not radial loads.
Thrust ball bearing composition
Thrust ball bearing composition: Thrust ball bearing consists of three parts: seat washer, shaft washer and steel ball cage assembly. The shaft washer matched with the shaft and the seat ring matched with the housing.
Thrust ball bearing types
According to the force, it is divided into one-way thrust ball bearings and two-way thrust ball bearings. One-way thrust ball bearing can bear one-way axial load. Two-way thrust ball bearing can bear two-way axial load, in which the shaft ring is matched with the shaft. Bearings with a spherical mounting surface of the seat ring have self-aligning performance and can reduce the influence of mounting errors. Thrust ball bearings cannot bear radial loads and have a low limit speed.
Thrust ball bearing features
- There are two types of one-way and two-way. 2. In order to tolerate installation errors, whether it is one-way or two-way, you can choose spherical self-aligning spherical seat type or spherical seat type. 3. High-quality steel – Ultra-clean steel that can extend bearing life up to 80% 4. Advanced grease technology – NSK’s lubricant technology extends grease life and improves bearing performance 5. High-grade steel balls – Quiet and smooth rotation at high speed 6. With the optional ferrule, installation error can be tolerated.
Thrust ball bearing application
The use of thrust ball bearings: It is only suitable for parts that bear an axial load on one side and have a low speed, such as crane hooks, vertical water pumps, vertical centrifuges, jacks, low-speed reducers, etc. The shaft washer, seat washer and rolling element of the bearing are separated and can be assembled and disassembled separately.
Thrust ball bearing assembly
There are two key points in the assembly of thrust ball bearings. One is the control of the pressing quality of the cage and the steel ball, and the other is the control of the nominal height T after the bearing is assembled. In addition, since the shaft ring and the seat ring can be separated, it brings a management problem.
It is to prevent the mixing of imported bearing parts. The M-type stamping cage uses a flanged assembly die. After pressing, the steel ball is required to rotate flexibly in the pocket, but it cannot fall off from the pocket, and the technical regulations check the amount of movement of the steel ball in the pocket. If the solid cage is imprinted too deeply, the movement of the steel ball will be small, and the connection between the embossed convex part and the cage is too small and the strength is insufficient, which is prone to the phenomenon of falling blocks, causing the cage to be scrapped.
There is little difference between the inner diameter of the small thrust ball bearing seat washer and the shaft washer, and there is no obvious difference between the two sets. In order to prevent the phenomenon of mixed sets, it is found that two sets of bearings are both seat washers or shaft washers in the assembled set of bearings.
This requires certain measures. Usually, the drawing ring and the seat group are distinguished by auxiliary tooling when the sleeve is assembled, or the inner diameter size is checked with an inner diameter plug gauge before sampling the nominal height.
For the convenience of checking the inner diameter, put the seat ring on the bottom and the shaft ring on the top. If the inner diameter of the seat ring has obvious quenching heating oxidation color or has not been ground, it is not necessary to check the inner diameter size, and the difference between the shaft washer and the seat ring can be clearly seen, and it is not easy to mix. After the thrust ball bearing is assembled, the nominal height T needs to be measured to confirm whether it is qualified. When measuring, calibrate with a height block or standard part, and measure the load, the bearing needs to be rotated dozens of times, and the minimum height must be reached.
When the thrust ball bearing operates at high speed, the contact angle between the steel ball and the radial plane of the raceway will be affected by centrifugal force, which will cause the sliding of the steel ball relative to the raceway. Adhesive wear from this sliding can damage the bearing. To prevent this damage, the minimum load on the thrust ball bearing must be guaranteed, see Equation 1 or Equation 2, whichever is the larger of the calculated values.
Formula 1: Famin=K?n*n
Formula 2: Famin=Coa/1000
Famin: Minimum axial load (N)
K: Minimum axial load factor
n: rotation speed (per minute)
Coa: Basic static load rating (N)
The one-way thrust ball bearing can only bear the load in one direction, if it bears the load in two directions, the two-way thrust ball bearing must be selected. Thrust ball bearings must have a minimum load or preload applied. When the shaft is vertical, the weight of the shaft usually exceeds the minimum load. At this time, the acting load may be reduced due to the influence of the axial external load in the opposite direction.
Thrust ball bearings are separable bearings with a contact angle of 90°, which can only bear axial loads and have a low limit speed.
1. Main structure type
(1) One-way thrust ball bearing type 51000 This type of bearing can only bear the axial load in one direction, and can limit the axial movement of the shaft and the housing in one direction.
(2) Two-way thrust ball bearing type 52000 This type of bearing can withstand axial loads in two directions, and can limit the axial movement of the shaft and the housing in two directions.
2. Cage material
When the outer diameter of the thrust ball bearing is D≤250mm, a steel plate (or belt) stamping cage is generally used; when the outer diameter D>250mm, a solid cage is used.
3. Minimum axial load
During the operation of the thrust ball bearing, if the external axial load is too small, the bearing is not compressed. Due to the action of inertial force, the steel ball will slip and destroy the normal operation of the bearing. Therefore, a certain axis must be applied to the bearing. To load, the minimum value is calculated as follows: Famin=A(n/1000)2
In the formula: Famin minimum axial load (kN); A-minimum load constant n speed (r/min).
The minimum load constant, A, is listed in the bearing dimension table. If the external axial load is too small, the bearing can be preloaded with a spring.
4. Allowable inclination angle
To ensure verticality, the two bearing surfaces of the thrust ball bearing must be parallel, and no deviation is allowed. If the shaft centerline and the bearing surface of the housing cannot be guaranteed, spherical seat rings and self-aligning washers can be used to compensate.
5. Tolerance
Thrust ball bearing tolerances are listed on page 35.
6. Axial equivalent dynamic load
Thrust ball bearing can only bear axial load, and its axial equivalent dynamic load is: Pa=Fa
7. Axial equivalent static load
The axial equivalent static load of the thrust ball bearing is: Poa=Fa
Main structural features and related parameters of two-way angular contact thrust ball bearings
Bidirectional angular contact thrust ball bearings are used together with double row cylindrical roller bearings to withstand bidirectional axial loads. The bearing consists of two shaft washers, a seat washer, a spacer, two rows of rolling elements and a cage
The clearance and preload of the bearing can be adjusted by grinding the thickness of the spacer, and the contact angle of the bearing is 60°. The nominal outer diameter of this kind of bearing is the same as that of the matching double row cylindrical roller bearing with the same bore diameter, but the outer diameter tolerance zone is below the zero line, and there is a gap between it and the shell, so it does not bear radial load. Specially used for thrust bearings.
BEM bidirectional angular contact thrust ball bearings have the advantages of high precision, good rigidity, low temperature rise, high speed, and convenient loading and unloading.
In order to facilitate effective lubrication, a lubricating oil groove is provided on the bearing seat ring, and a lubricating hole is opened in the middle.
2344 and 2347 series bearing structure as shown. 2344 series bearings should be installed on one end of the cylindrical roller bearing with a smaller diameter (tapered hole), and 2347 series bearings should be installed on the side with a slightly larger taper diameter. Example of bearing code: 234420M.SP 234720M.SP
Grease lubrication
The operation of the two-way angular contact thrust ball bearing can achieve its purpose of lubrication. Because the required amount of lubricant is larger than that of adjacent cylindrical roller bearings, it should be noted that the oil can not all flow into the cylindrical roller bearing during design, and sufficient lubricant should be ensured for the two-way angular contact thrust ball bearing.
Bearing Preload and Rigidity
For the spacer sleeve between the two shaft rings of the bidirectional angular contact thrust ball bearing, a gap can be formed by grinding the thickness of the spacer sleeve 1, so as to ensure that the bearing will obtain a suitable axial preload after installation. The preload should not be too large so as not to twist the gap sleeve and cause a larger preload.
Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings for Ball Screws
Angular contact thrust ball bearings are specially designed for ball screw bearing configuration, and have the characteristics of high precision, high speed, high axial stiffness, low friction, long life and good instantaneous high and low speed conversion performance. Its size series are 7602, 7603 and BSB (non-standard metric), with inner diameters from 12mm to 130mm.
The BEM ball screw bearing is a one-way angular contact thrust ball bearing with a contact angle of 60°, which can bear a large axial load in a single direction, and can also bear a certain radial load. Usually, the bearings need to be used in groups, and the configuration is the same as that of angular contact ball bearings. See “Bearing dimension table” for preload value, not marked in the code.
The bearing set is composed of bearings with matching outer and inner diameters, and the representation method is shown in “Code of Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings for Ball Screws”.
Example of bearing code:
7602035TVP.P4.DB
7602035TVP.P4.TBT
7602035TVP.P4.QBC
BSB025062TVP.P4.DB
BEM also provides general-purpose angular contact thrust ball bearings, which are indicated in “Code of Angular Contact Ball Bearings for Ball Screws”.
Example of universal bearing code:
7602035TVP.P4.DU
7602035TVP.P4.TU
7602035TVP.P4.QU
BSB025062TVP.P4.DU
Angular contact thrust ball bearings for ball screws: The requirements of the ball screw on the bearing are the same as those of the main shaft and the transmission shaft, that is, sufficient accuracy and speed should be guaranteed, the difference is that the screw bearing bears The load is mainly axial. Therefore, the axial accuracy and rigidity of the screw bearing are required to be high. The feed system requires flexible movement and sensitive response to small displacements (small rotation angles of the lead screw). Therefore, the friction torque of the bearing should be as low as possible.
At present, the most used ball screw bearings are angular contact thrust ball bearings with a contact angle of 60°, followed by needle roller and thrust roller combined bearings. The latter are mostly used in large and heavy machine tools that require high rigidity.
Grease lubrication
Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings for Ball Screws These bearings are lubricated with grease, and the amount of grease filling is shown in the “Bearing Dimensions Table”. For operation refer to the practice of angular contact ball bearings.
Bearing Preload and Rigidity
Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings for Ball Screws Angular contact thrust ball bearings with a contact angle of 60° can withstand combined loads mainly from axial loads. Like angular contact ball bearings, these bearings are often used in pairs or groups and preloaded. See bearing dimension table for preload and axial stiffness.
Bearing speed limit
Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings for Ball Screws are greased with allowable rotational speeds as shown in the sample bearing dimension table, and are suitable for back-to-back or face-to-face arrangements. As for other bearing arrangements, the limit speed will be reduced.